有時候後端要執行一個時間比較長的任務,而任務內容極為複雜,又容易出錯,因此希望讓使用者看到即時的 console log,讓我們函式中的 print 輸出能即時傳到使用者的瀏覽器。
以下將會以 Django, Thread, Queue 進行實做
StreamingHttpResponse
一般的網頁請求都是一次打包好所有資料,全部傳給使用者,有些情況我們不能等到所有資料準備好才一次傳,而要拿到一些就傳一些,這個時候我們就要使用串流輸出,在 Django 裡,就是使用 StreamingHttpResponse,以下簡稱 SHR。SHR 接收一個 Iterator 作為輸入,因此我們只要實做一個迭代器函式,其中每次 yield 就會由 SHR 傳送到瀏覽器
# Example of StreamingHttpResponse
from django.http.response import StreamingHttpResponse
def example():
for i in range(5):
# Add <br> to break line in browser
yield f'{i}<br>'
def stream(request):
return StreamingHttpResponse(example())
Output (in browser):
0
1
2
3
4
Thread
由於我們的程式需要一邊執行目標任務,一邊串流輸出,因此需要平行化執行。Python 中可以使用 threading, multiprocessing 等方式做平行化執行,本文將使用 threading。
# Example of threading
from threading import Thread
import time
def example(times):
for i in range(times):
print(i)
time.sleep(1)
# 建立 Thread
thread = Thread(target=example, args=(5,))
# 啟動 Thread
thread.start()
time.sleep(2)
print("This is printed in main thread")
# 等待 thread 完成
thread.join()
Output:
0
1
This is printed in main thread
2
3
4
重新導向 Stdout
Python 中 print 的輸出稱之為 stdout – Standard Output 標準輸出,簡單來說就是輸出到終端機的內容。要改變 print 的輸出位置,我們就要改變 sys.stdout 這個變數,stdout 可以接受任何 File-like 的物件,具體而言就是實做了 write 方法的物件。
# Example of redirect stdout
import sys
class Printer:
def __init__(self):
self.contents = []
def write(self, value):
self.contents.append(value)
printer = Printer()
sys.stdout = printer
print('This should be saved in printer')
sys.stdout = sys.__stdout__
print('This should be printed to stdout')
print(printer.contents)
Output:
This should be printed to stdout
['This should be saved in printer', '\n']
實做串流輸出 Stdout
環境
Python 3.8.5
Django 3.2
首先建立一個 Django Project
pip install django
django-admin startproject console_streaming
cd console_streaming
python manage.py startapp web
安裝 web:
# console_streaming/settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
# 加入 web
'web',
]
建立 view:
# web/views.py
def stream(request):
# 待會實做
pass
綁定到 urls:
# console_streaming/urls.py
from django.urls import path
from web import views
urlpatterns = [
path('stream/', views.stream),
]
測試函式
這是我們用來模擬目標任務函式,重複 times 次的 print 出一行字,並等待一秒,最後 print 出 “Done”。
# web/views.py
import time
def job(times):
for i in range(times):
print(f'Task #{i}')
time.sleep(1)
print('Done')
time.sleep(0.5)
Printer class
以下實做一個 Printer 來處理所有的 stdout,並且整個程式生命週期只用一個 instance,原因是 sys.stdout 是不分 thread 的,因此如果不同的 request 使用不同的 printer,會搶走別人的 stdout。因此我使用一個 map 來儲存不同 thread 的 queue,並用 current_thread() 來判斷當前的 thread 取出正確的 queue。而假如當前的 thread 沒有註冊到 Printer,則使用 stdout 輸出。
# web/views.py
from queue import Queue
from threading import current_thread
import sys
class Printer:
def __init__(self):
self.queues = {}
def write(self, value):
'''handle stdout'''
queue = self.queues.get(current_thread().name)
if queue:
queue.put(value)
else:
sys.__stdout__.write(value)
def flush(self):
'''Django would crash without this'''
pass
def register(self, thread):
'''註冊一個 Thread'''
queue = Queue()
self.queues[thread.name] = queue
return queue
def clean(self, thread):
'''刪除一個 Thread'''
del self.queues[thread.name]
# 初始化一個 Printer instance
printer = Printer()
sys.stdout = printer
Streamer class
接下來要實做併發執行以及回傳 StreamingHttpResponse,我將併發執行的部份寫成一個 Streamer class,其會初始化一個 Thread,將其註冊到 printer 取得 queue,接著不斷讀取 queue 的內容,將內容 yield 到 StreamingHttpResponse,直到 thread 結束。
from threading import Thread
class Steamer:
def __init__(self, target, args):
self.thread = Thread(target=target, args=args)
self.queue = printer.register(self.thread)
def start(self):
self.thread.start()
print('This should be stdout')
while self.thread.is_alive():
try:
item = self.queue.get_nowait()
yield f'{item}<br>'
except Empty:
pass
yield 'End'
printer.clean(self.thread)
def stream(request):
streamer = Steamer(job, (10,))
return StreamingHttpResponse(streamer.start())
執行 Django
$ python manage.py runserver
打開 http://localhost:8000/stream/
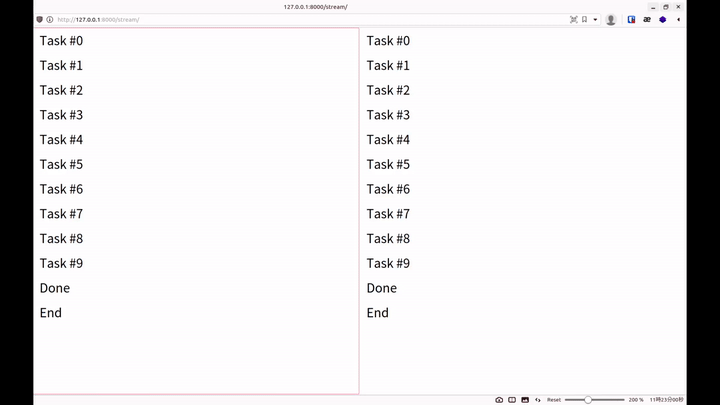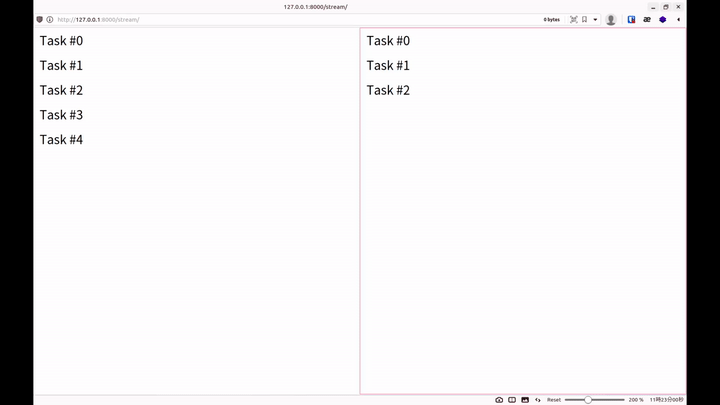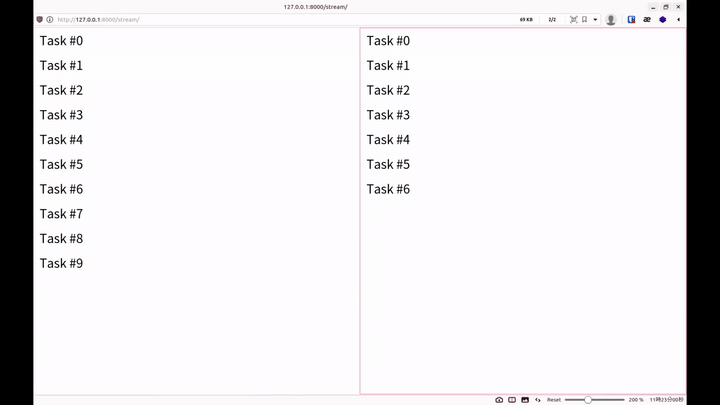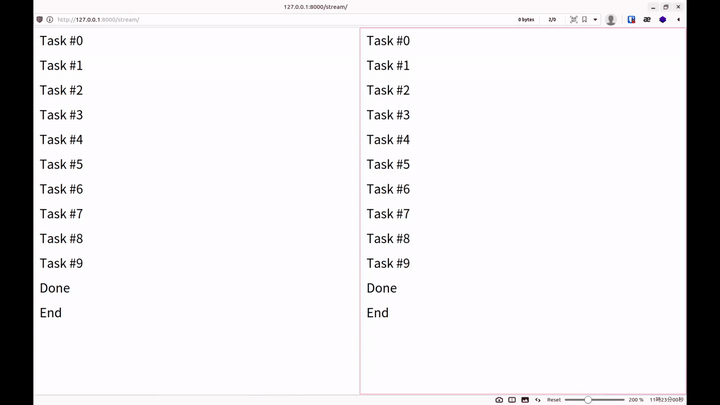
就能看到像是以下的輸出

而每新增一個請求,終端機就可以看到一行
This should be stdout
完整 views.py
from django.http.response import StreamingHttpResponse
from queue import Queue, Empty
from threading import Thread, current_thread
import time
import sys
class Printer:
def __init__(self):
self.queues = {}
def write(self, value):
'''handle stdout'''
queue = self.queues.get(current_thread().name)
if queue:
queue.put(value)
else:
sys.__stdout__.write(value)
def flush(self):
'''Django would crash without this'''
pass
def register(self, thread):
'''註冊一個 Thread'''
queue = Queue()
self.queues[thread.name] = queue
return queue
def clean(self, thread):
'''刪除一個 Thread'''
del self.queues[thread.name]
printer = Printer()
sys.stdout = printer
class Steamer:
def __init__(self, target, args):
self.thread = Thread(target=target, args=args)
self.queue = printer.register(self.thread)
def start(self):
self.thread.start()
print('This should be stdout')
while self.thread.is_alive():
try:
item = self.queue.get_nowait()
yield f'{item}<br>'
except Empty:
pass
yield 'End'
printer.clean(self.thread)
def job(times):
for i in range(times):
print(f'Task #{i}')
time.sleep(1)
print('Done')
time.sleep(0.5)
def stream(request):
streamer = Steamer(job, (10,))
return StreamingHttpResponse(streamer.start())
完整程式碼:GitHub